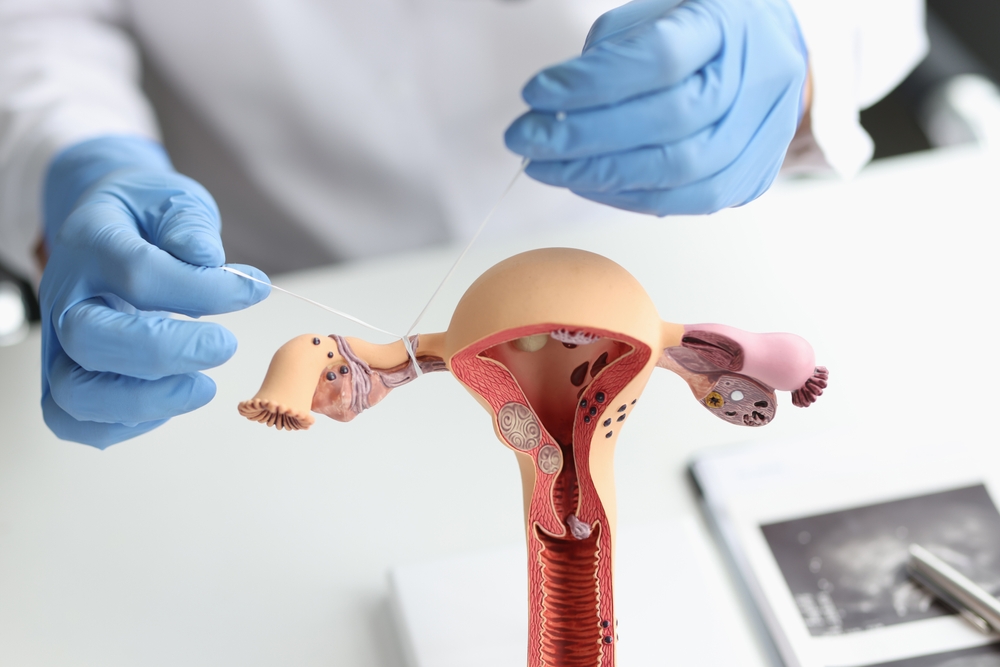
Tubal ligation, commonly referred to as “having your tubes tied,” is a surgical procedure where the fallopian tubes are sealed or blocked to prevent pregnancy. It’s a decision many women make when they feel their family is complete or for medical reasons. But for young women, what happens after tubal ligation? Is there a way to get pregnant after tubal ligation? Yes! We’ll explain how to have a baby after your tubes have been tied and why tubal ligation is not a permanent solution to unwanted pregnancy.
V Fertility Center is a fertility clinic in Thailand that offers IVF and ICSI services at Vejthani Hospital. We’ll explore the details of the procedure and why it’s become popular.
What Happens During Tubal Ligation?
During a tubal ligation, a surgeon blocks, seals, or cuts the fallopian tubes, preventing the egg from traveling from the ovaries to the uterus. This can prevent pregnancy by stopping the sperm from reaching the egg. However, women, on occasion, have become pregnant naturally after a tubal ligation. The fallopian tubes are still living parts of the human body, and they can grow back and reestablish a pathway for sperm to reach an egg.
Dangers of Tubal Ligation
While tubal ligation is generally effective in preventing pregnancy, approximately 1 out of 200 women who undergo tubal ligation may experience an ectopic pregnancy. This happens when a fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus, mainly in the fallopian tubes. Although low, it’s crucial to be aware of this risk when considering tubal ligation. Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- Abdominal pain
- Light vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain and pressure during a bowel movement
Women experiencing any of these symptoms should see a doctor immediately, as the fallopian tube can rupture and cause internal bleeding.
Can You Still Get Pregnant After Tubal Ligation?

Natural pregnancy occurs in one per cent of women after a tubal ligation, and the chances of pregnancy continue to reduce as they age. However, the chances of becoming pregnant after tubal ligation increase significantly through a comprehensive IVF program.
Exploring Pregnancy Options with IVF
One of the most viable options for becoming pregnant after tubal ligation is in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF involves fertilizing an egg with sperm outside the uterus and then implanting the fertilized embryo directly into the uterus. This bypasses the blocked fallopian tubes, making pregnancy possible.
IVF often includes intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). ICSI is an assisted reproductive technique where the single most motile and healthy sperm is selected and injected directly into a fertile ovum to increase the chances of fertilization. The resulting embryo is then grown in an embryology lab until it reaches the day-5 Blastocyst stage, when it’s transferred into the womb to continue its development.
Why Choose IVF at V Fertility Center?
At V Fertility Center, we offer cutting-edge IVF treatments to help individuals achieve their dream of parenthood. Our state-of-the-art facilities, combined with the latest reproductive technology and advanced medical and surgical care standards, ensure that every patient receives personalized and comprehensive fertility care.
With our team of experienced fertility specialists, we guide patients through every step of the IVF process. From initial consultation to embryo transfer, we provide compassionate support and expert guidance to maximize your chances of success.
Take the Next Step
If you’re considering pregnancy after tubal ligation, consulting a fertility specialist is the first step. Our team at V Fertility Center in Bangkok is here to answer your questions, address your concerns, and develop a customized treatment plan.
Don’t let tubal ligation deter you from your dream of becoming a parent. Contact us today to schedule a consultation with our fertility experts and explore the possibilities of IVF after tubal ligation.
Article by Dr. Worawat Siripoon

OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY-REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE





No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.